He started with a little diagram to explain how Aristotle thought that all matter consisted of four elements: Earth, Air, Water, and Fire. and these had 4 qualities: Dryness, wetness, coldness, and hotness.
Everyone believed that until Democritus improved his idea. Democritus believed atoms were indivisible (which was right), and he thought each different thing was made of different substances, not just the four elements. He foreshadowed that there were more elements and that they were indivisible. Then he split us up in groups by choosing 7 "team captains" and having them choose one by one their teams, then switching the captains to a team they didn't make. to explain the rest of the atomin theories.
First came Dalton's model. He said that elements have/composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. Also, that the atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass, and chemical properties, and they differ from atoms of different elements. Another thing he said was that all chemical reactions are changes in the proportions of atoms. (Which were all correct thoughts.)
Then in 1897 the Atom was observed for the first time in England. And with came the Electron and Thomson's model He discovered Electrodes: anodes are negative and catons are positive. He realized that electrons move very fast and have negative charges. Which is of 1.602x10^-10.
Radioactivity is a phenomenon where atoms decompose spontaneously. It was discovered accidentally by Henry Bequetel in 1892. Radioactive elements are polanium and radium. The different types of radiation are:
Alpha: Lowest penetrability
Beta:Moderate penetrability
Gamma: High Penetrability
Next was Rutherford's modela nd the Nucleus. Rutherford's theory was that protons and electrons were evenly dispersed. He made an experiment where they shot alpha particles througha thin sheet of gol foil. If he had been correct the particle should've gone straight thorugh unhindered, but since he was mistaken some defleted as they passed through and others bounced back. With that he came up with another atomic model
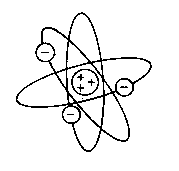
In his model protons would be concentrated in a small space and the electrons would be orbiting the empty space around them, and the area where the protons where was called the neutron His model is often called the planetary model becaus of its resemblance to the planets orbiting the sun. The diameter of a typical atom is about 10,000 times greater than the diameter of a typical nucleus. So if the atom was the size of a football field the nucleus would only be the size of a grape.
Then came Bohr's Model. WHich was a proposed quantized shell model og the atom to explain how electrons can have stable orbits around the nucleus: The Quantum Model. It's principles are:
-An atom is composed by a very small nucleus which is a positive charge (Just like Rutherford's model)
-The electrons of an atom can only exist in "special" energetic shells or orbits around the nucleus and can have the names of 1. 2. 3 or K, L, M etc.
-The electrons have definite and characteristic energy according to the shell. K orbit has the lowest radio and energy because it is closest to the nucleus.
-Atoms have two energetic states: Ground state(Stable) and Excited state(too much energy).
When they are in the escited state they need to jump to the next orbit but by doing that they get tired and lose energy so they have to bounce back to their original orbit this movement is called a transition, and each jump has a characteristic light(emission spectrum) it gives out.

Then came Sommerfeld's model which was just Arnold Sommefeld's improved quantum model Saying that there was the same amount of protons and electrons, and that the shells could be circular or elliptical.
Then came the Modern Model which was established by Schrodinger and Dirac. It is a complex mathematical model. It is the result of integration of different knowledge. It sattes that electrons are distributed around the nucleus in probability regions called atomic orbitals. It is also called Quantum mechanical model. It was proposed because:
a. Albert Einstein explained the Photoelectric effect.
b. Louis De Broglie proposed that matter has a particle/wave duability.
c Werner Heinsberg proposed the Uncertainty Principle

And that was basically the whole class, just taking notes on the presentations. He did sat we should watch a video titled : "What the 'bleep' do we know?" to help understand it better.
Victoria Bracamontes

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario